Lipedema, also known as lipoedema, is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of painful adipose tissue, or fat, in specific body areas. While it primarily affects women, men can also develop lipedema under certain circumstances. This condition is often misdiagnosed as obesity or lymphedema, leading to confusion and delayed treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the stages, types, and symptoms of lipedema, shedding light on this often misunderstood disorder. As patients work through getting an official lipedema diagnosis, experts will first need to determine what lipedema stage the patient is currently at. There are three different lipedema stages, or levels of progression, used to evaluate how far the disease has progressed in the affected areas of the body – the first stage is the earliest onset, and the third stage is the most progressed.
What is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic disorder that causes an abnormal fat buildup in specific areas of the body, typically the legs. Unlike regular weight gain, which affects the entire body, lipedema predominantly impacts the lower body, resulting in a disproportionate appearance. This condition is characterized by pain, tenderness, and easy bruising in the affected areas. It is important to note that lipedema is a distinct condition and should not be mistaken for simple obesity.
The Three Stages of Lipedema
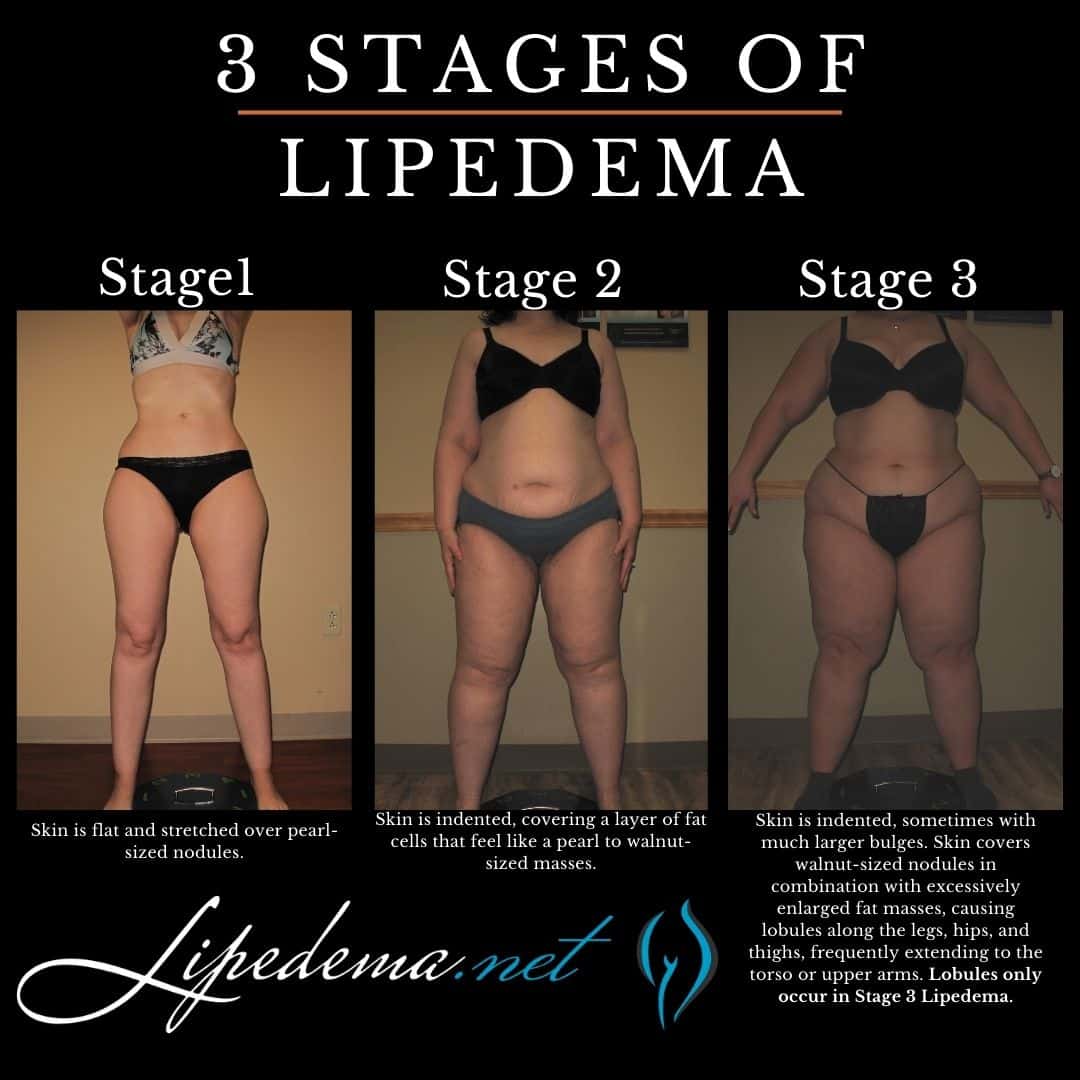
Lipedema is commonly categorized into different stages to evaluate the progression and severity of the condition. While the staging criteria may vary, the following stages provide a general overview of the disease. As lipedema progresses through these three stages, the level of pain, tenderness, swelling, and fat accumulation may increase. The images below provide an overview of the three lipedema stages, showing the location of fat build-up plus the resulting body shape at each stage. Depending on the person, different body parts can be affected in different ways at each stage.
Stage 1: Early Lipedema
In the early stage of lipedema, individuals may experience a smooth appearance of the skin in the affected areas. There is an increase in fat accumulation around the pelvis, buttocks, and hips. Swelling worsens throughout the day but typically resolves with rest and elevation. Symptoms may be mild moderate or severe with this stage.
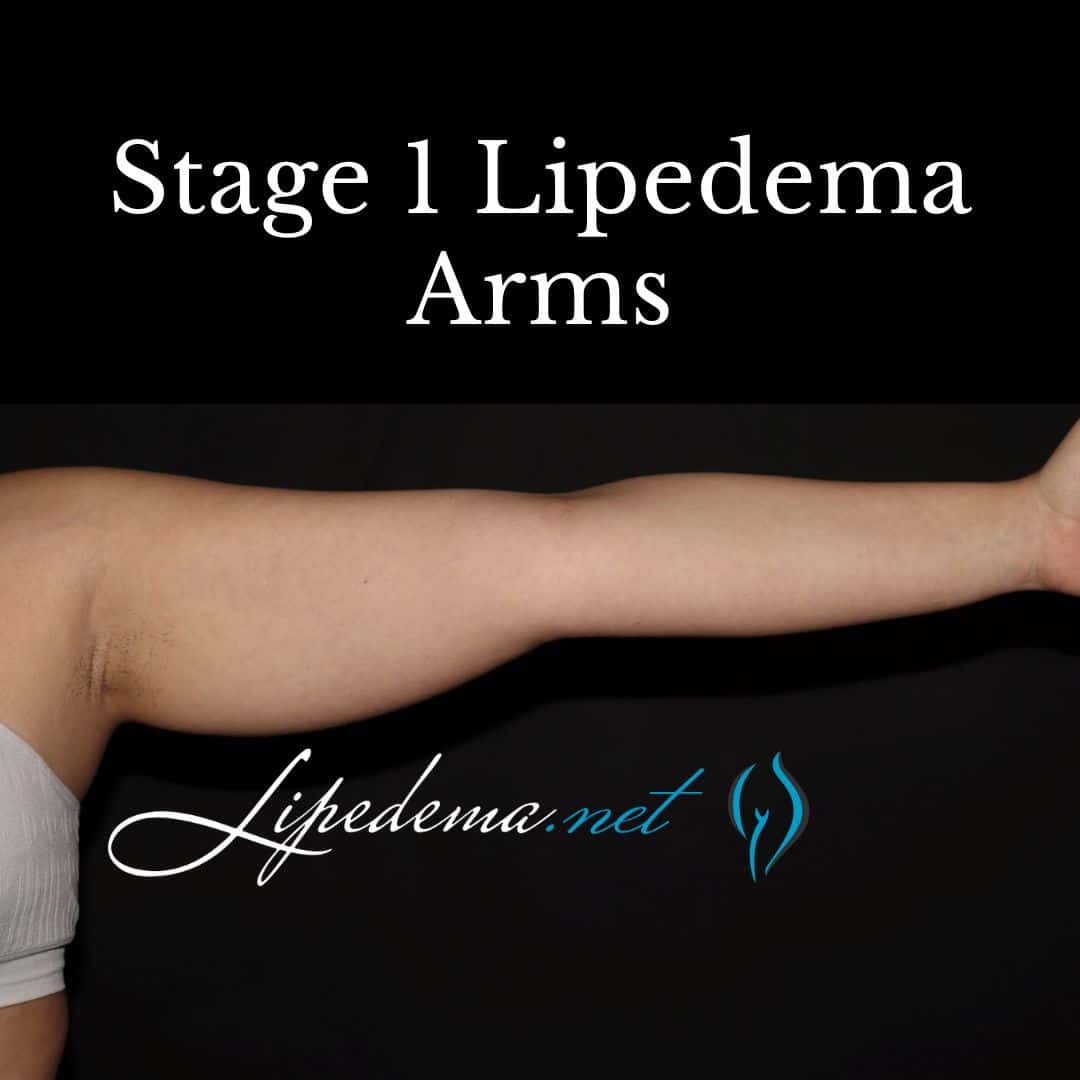
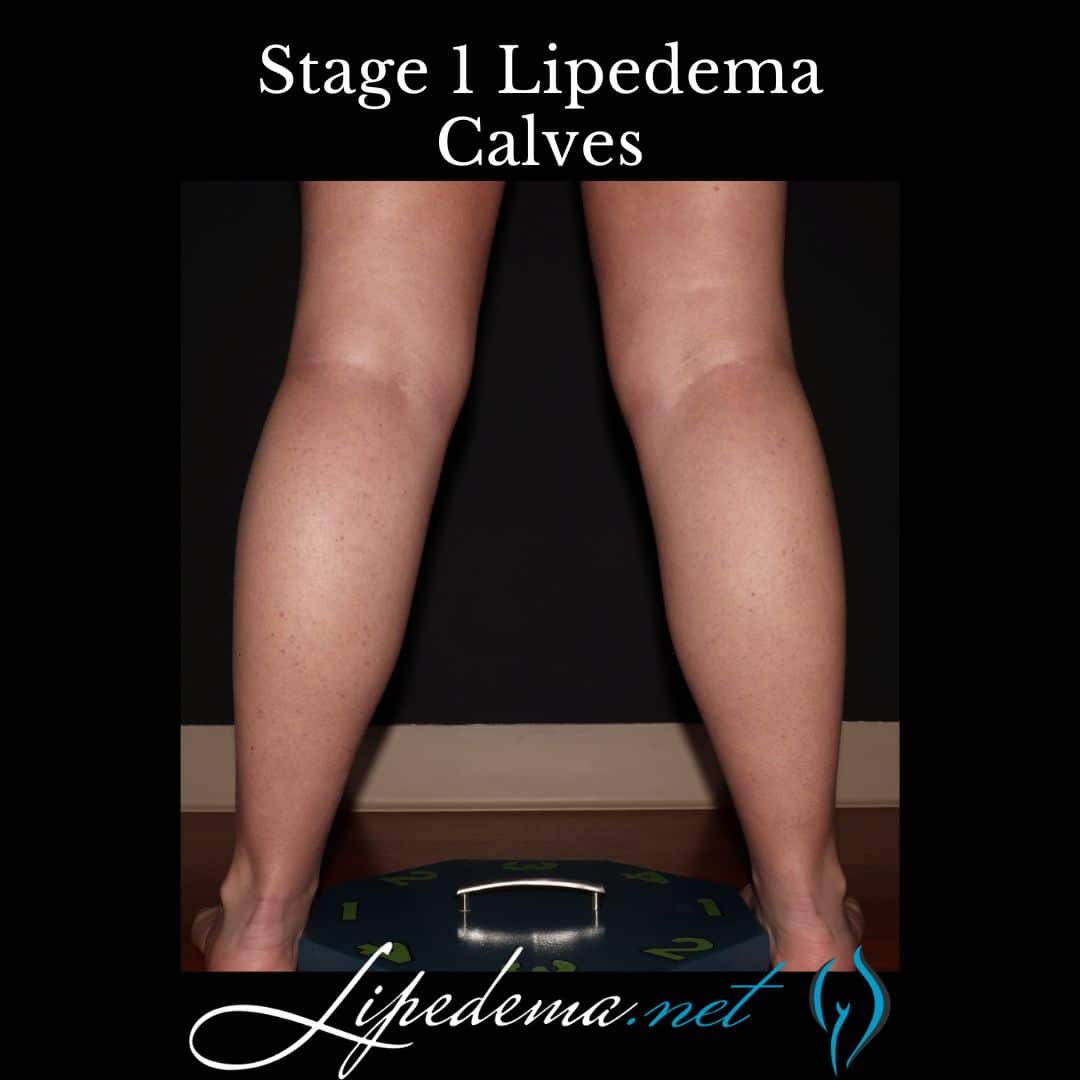
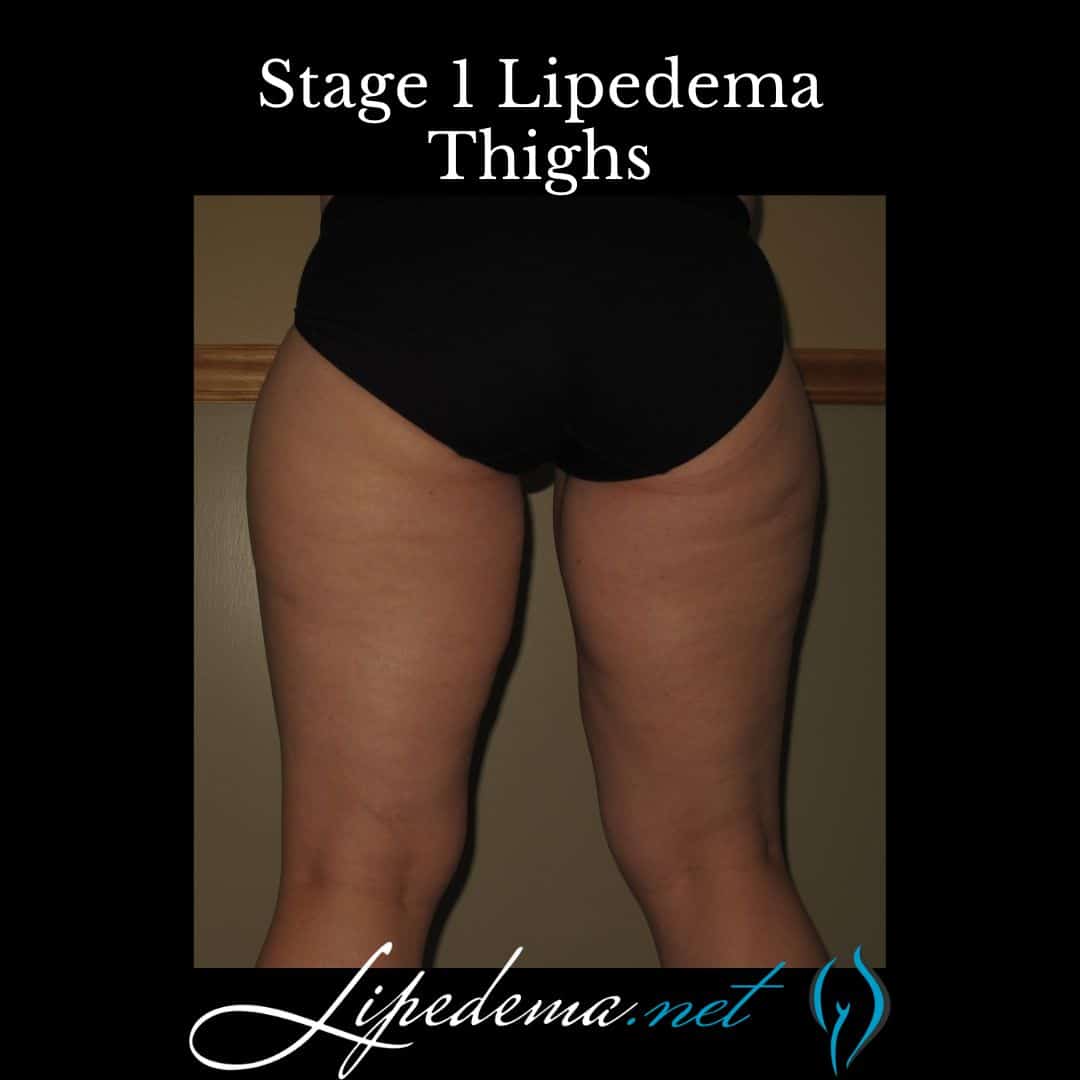
Stage 2: Mid-Stage Lipedema
As lipedema progresses, the skin develops indentations, and the subcutaneous tissue feels tougher and more nodular. Lipomas, or fatty lumps, may be present. Fat buildup becomes more noticeable on the upper and lower legs, extending towards the ankles. Swelling is often more significant in this stage. Swelling is less affected by rest and elevation compared to Stage 1. Symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe with this stage.
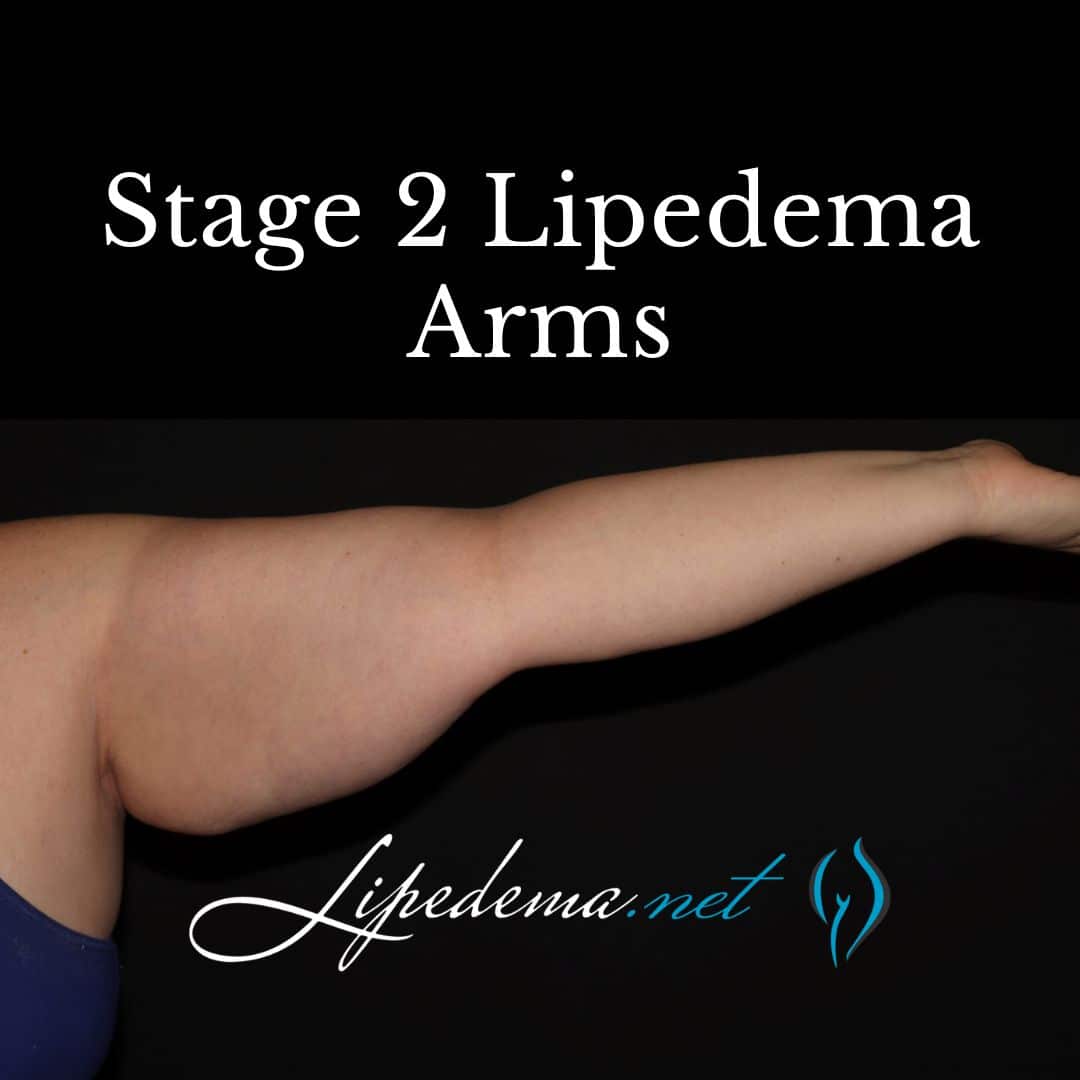
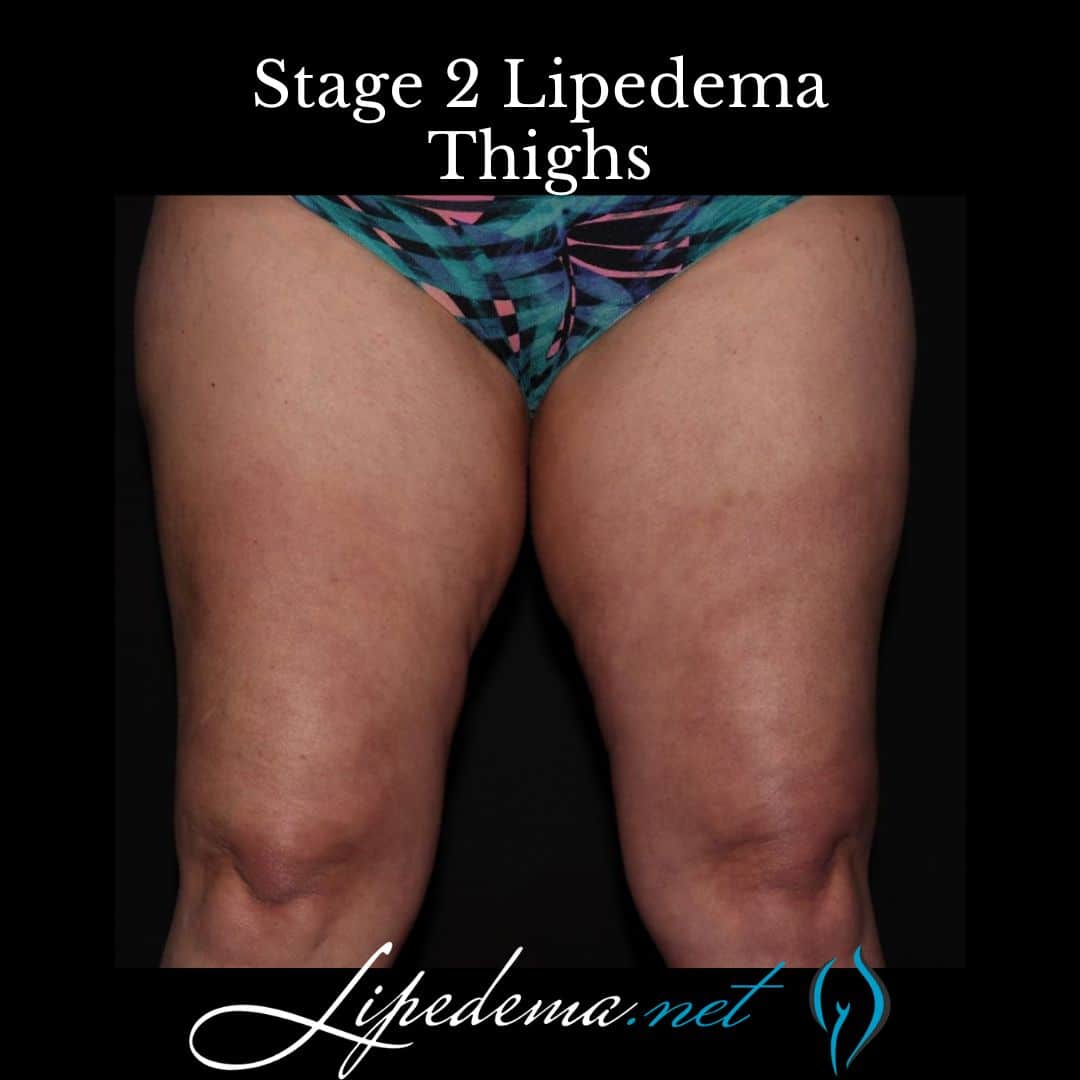
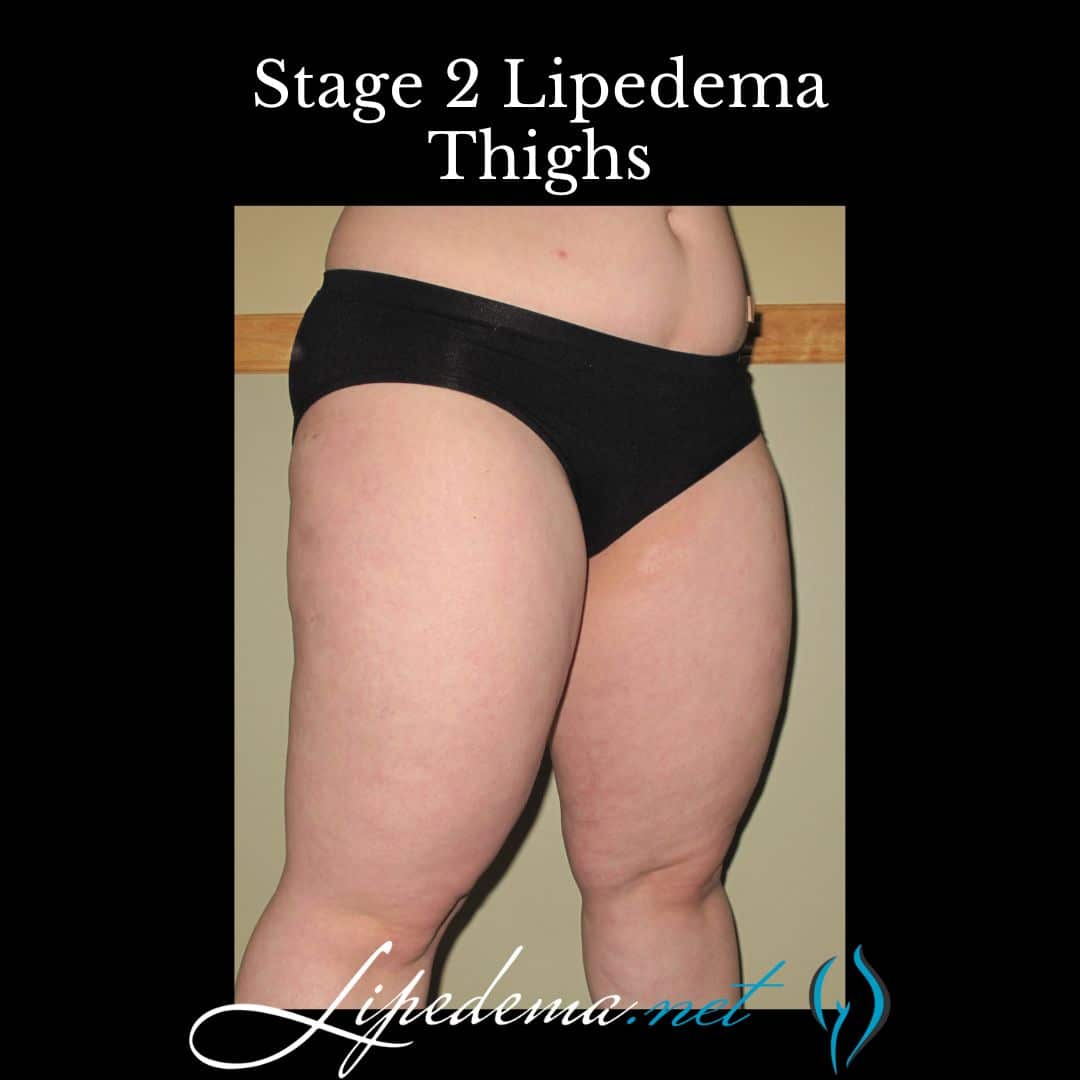
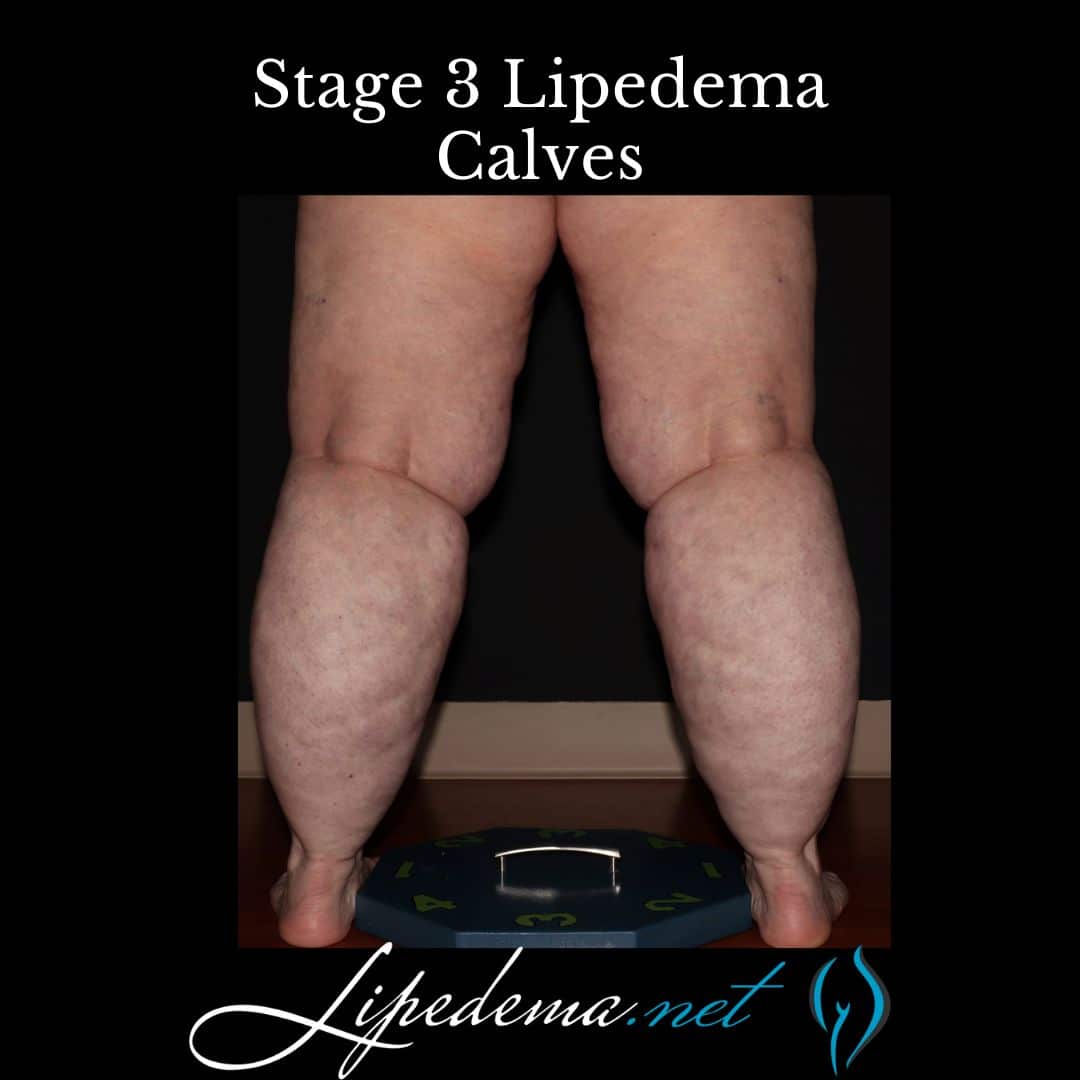
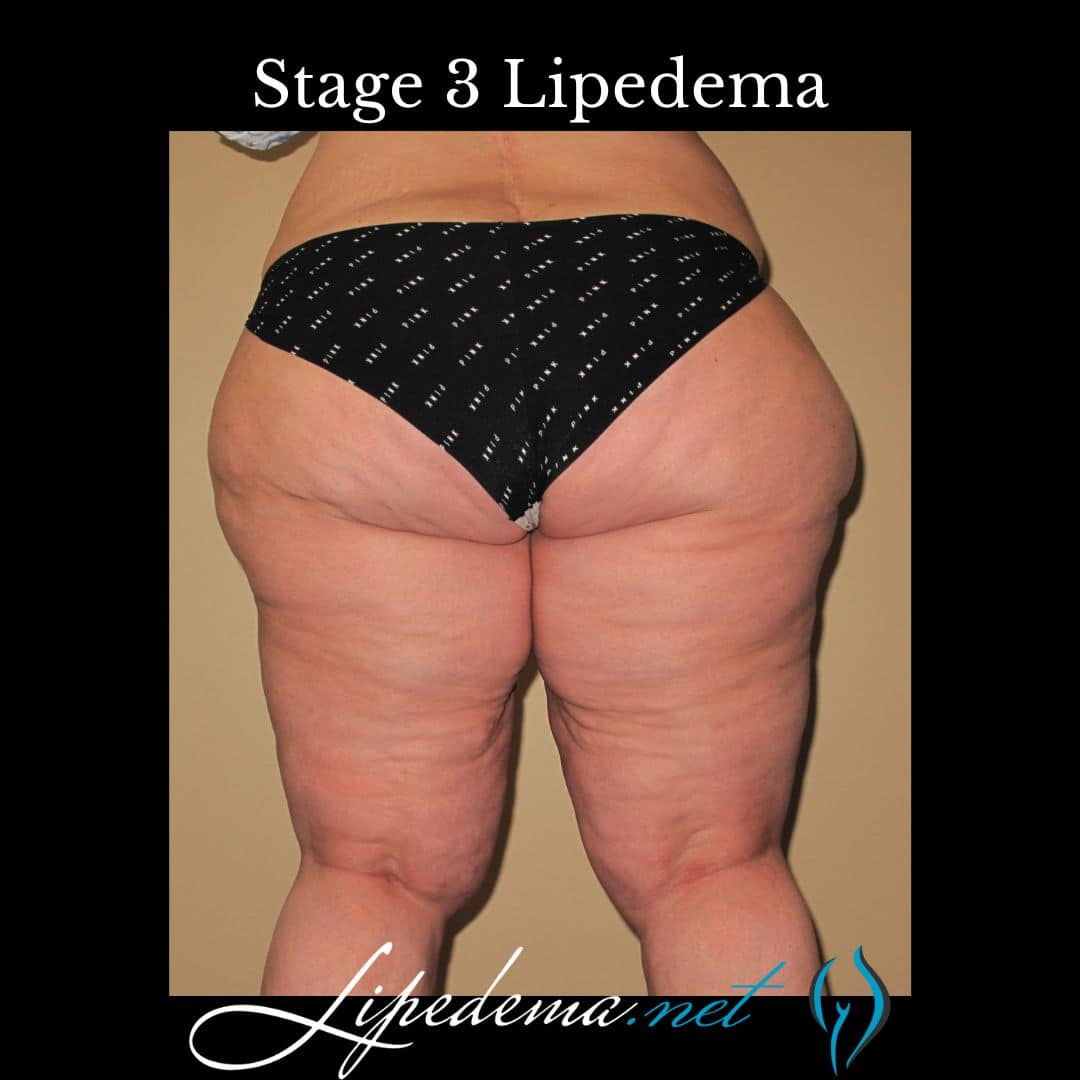
Stage 3: Advanced Stage Lipedema
In the advanced stage of lipedema, there is further hardening of connective tissues and persistent swelling that does not resolve with rest and elevation. Large masses of fat cause thigh and knee deformations, impacting mobility and quality of life. This stage may also be associated with the development of secondary lymphedema or secondary obesity. Stage 3 lipdema has the highest rate of orthopedic complications. Symptoms may be mild, moderate or severe with this stage.
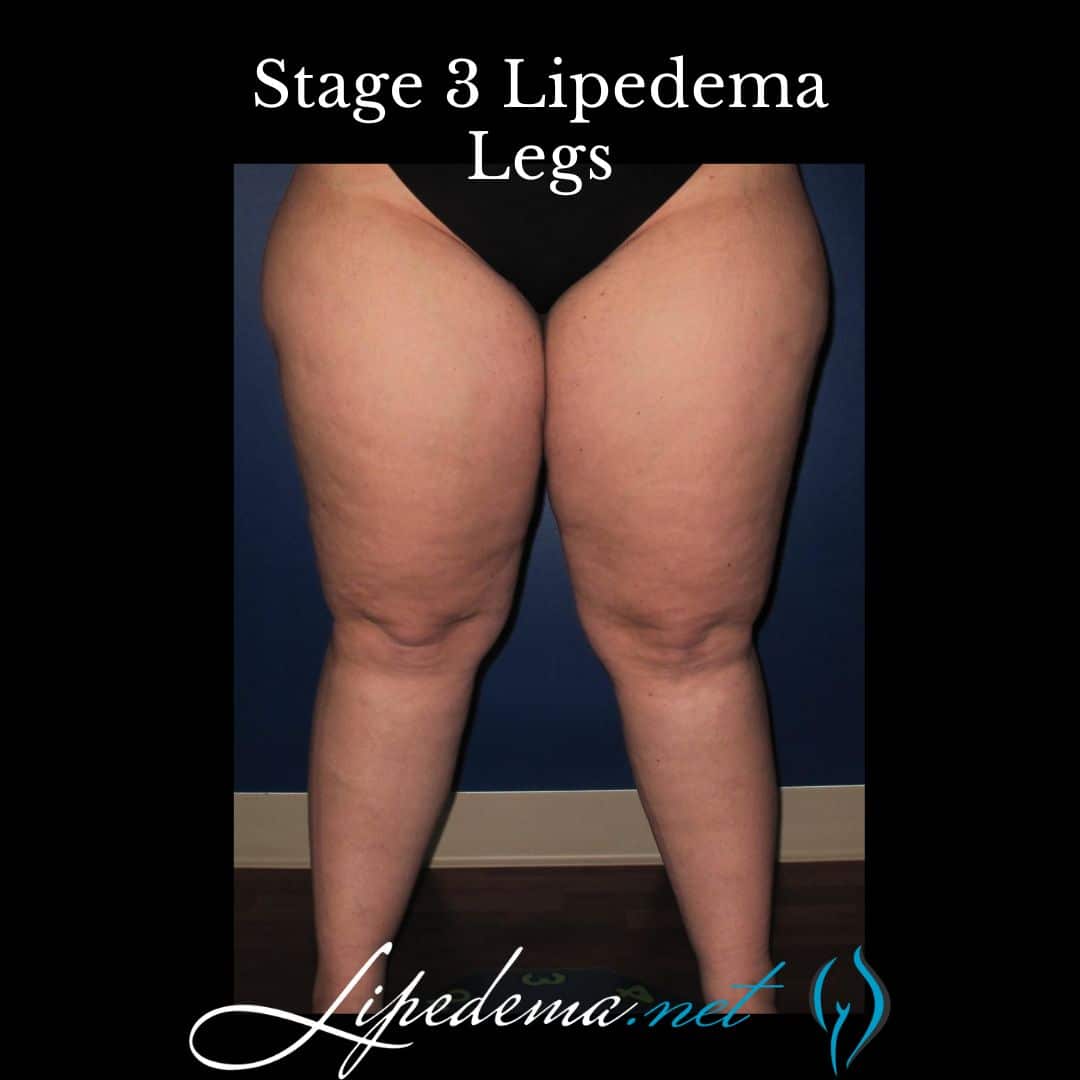
Where Did The Lipedema Stages Originate?
The first description of the Stages of lipedema appears in a German paper by Stößenreuther in 2001. In this paper, Stage 1 is classified as the early, “smooth” stage, Stage 2 as the visibility nodular stage, and Stage 3 as the lobular stage. In 2004, Schmeller also described similar stages of lipedema in 3 parts. Click here to see images of the early stages.
However, in a 2016 paper in PRS Global Open, Lipedema experts Buck and Herbst described the 4th stage of lipedema for the first time. As Buck and Herbst describe it, a would-be 4th stage of lipedema would be classified by the existence of
Lipolymphedema, or when there is a degree of secondary lymphedema from the lipedema. However, this supposes that lipedema edema progresses linearly with the stages, which clearly does not. Isabella Cordero, Gould, and Van De Pas have shown there are impaired lymphatic flow and function in stage 2 and stage 3 lipedema. Crescenzi showed that there is increased tissue sodium consistent with tissue edema in stage 2 and 3 lipedema. Therefore, there is no separate stage of lipedema 4 where lymphedema occurs; rather lymphedema or impaired lymphatics flow can occur in at least stages 2 and 3 lipedema.
Another important consideration of the stage of lipedema is that the stage of lipedema does not equal the severity of the lipedema. To put it another way, the stage of lipedema does not account for the volume of affected extremities the pain experienced by the individual, and do not consider the impairment of mobility or quality of life. In summary, the stages of lipedema are descriptive of the appearance of lipedema and are somewhat descriptive of the progression tissue, but do not fully describe the severity of the lipedema disease.
Do you have anorexia? Read about the link between lipedema and anorexia.
The 5 Types of Lipedema
Lipedema can manifest in different types based on the body’s fat distribution. While the lower body is commonly affected, lipedema can also involve the upper arms. The types of lipedema describe the body areas where the lipedema disease is present. More simply, these types refer to the location of the lipedema fat. The 5 types of lipedema were first described by Scmeller and Meier Vollrath, and the criteria by Meier-Volarath in 2007, as described below.
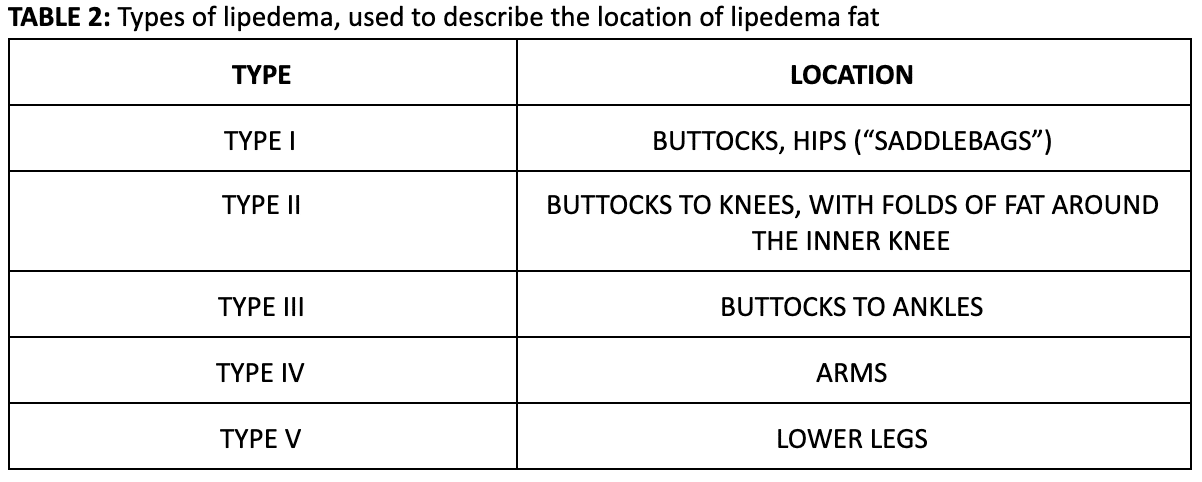
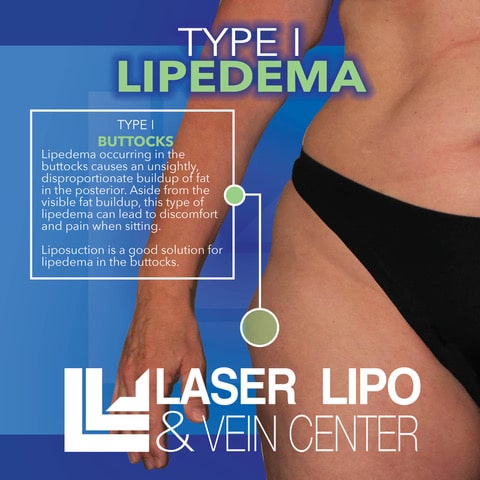
Type I: Buttocks and Hips
Type I lipedema primarily affects the area of the buttocks and hips, resulting in an accumulation of excess fat. This pattern of fat distribution gives rise to the characteristic saddlebag or jodhpur appearance.
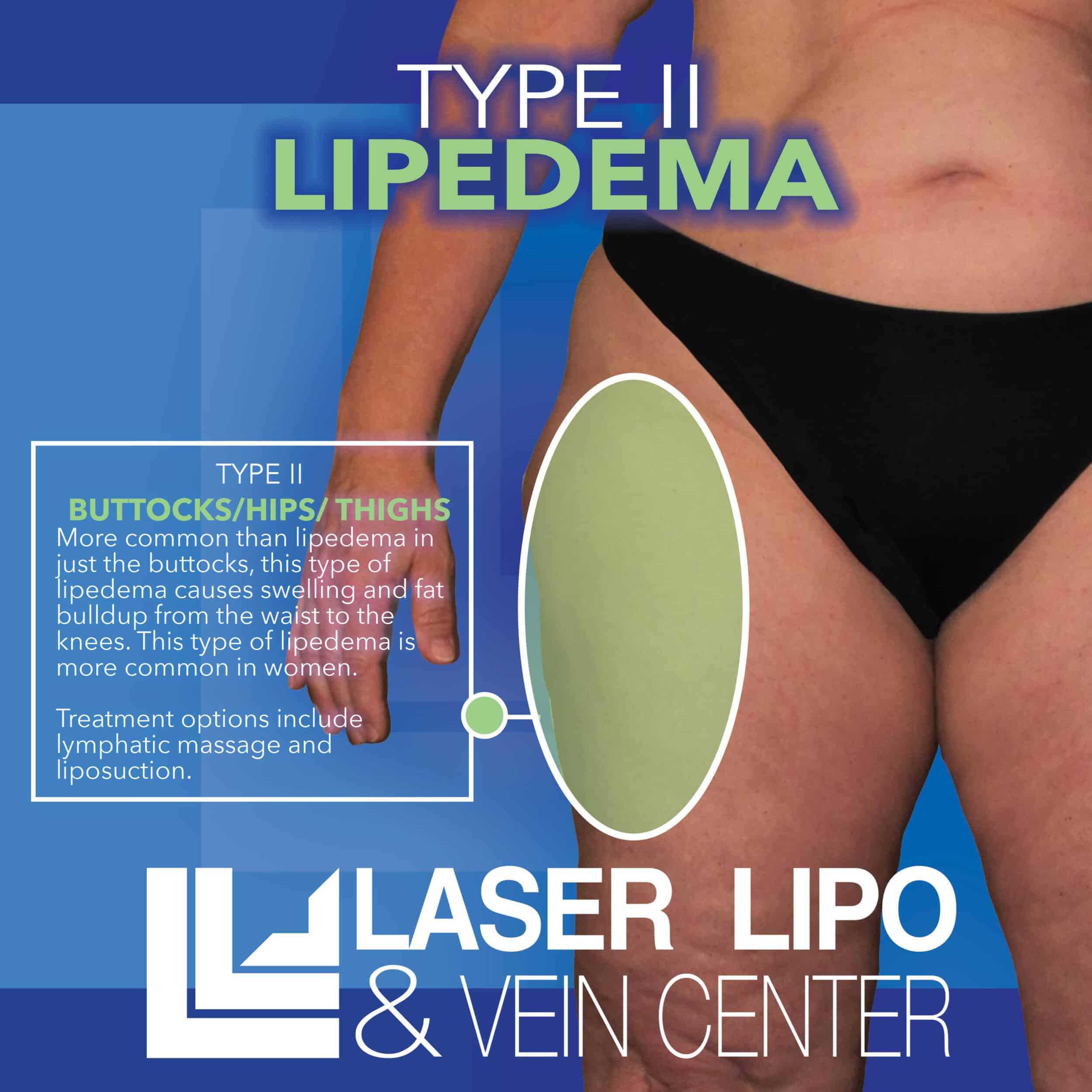
Type II: Buttocks to Knees
In Type II lipedema, fat buildup extends from the buttocks to the knees, with noticeable folds of fat around the inner side of the knee. This type may also involve the formation of lipomas within the fatty tissue.
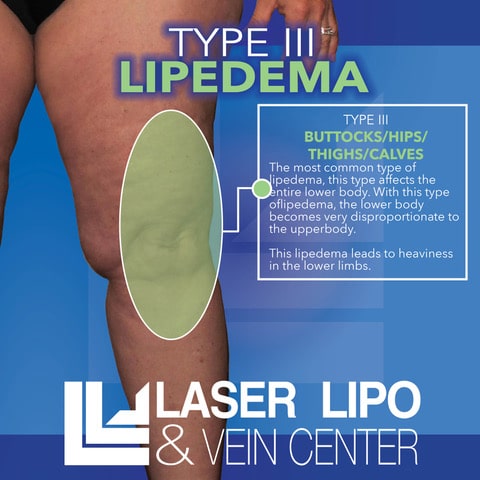
Type III: Buttocks to Ankles
Type III lipedema involves fat accumulation from the buttocks to the ankles. The lower legs and ankles may exhibit a collar of fat, while the feet remain unaffected.
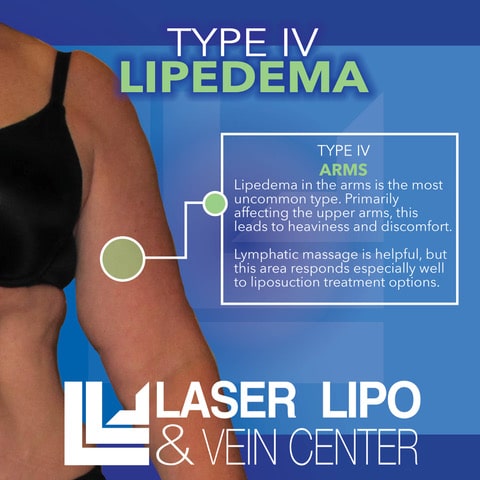
Type IV: Arms
Type IV lipedema affects the upper arms, leading to an abnormal accumulation of fat in this area. This type is less common but can significantly impact arm appearance and function.
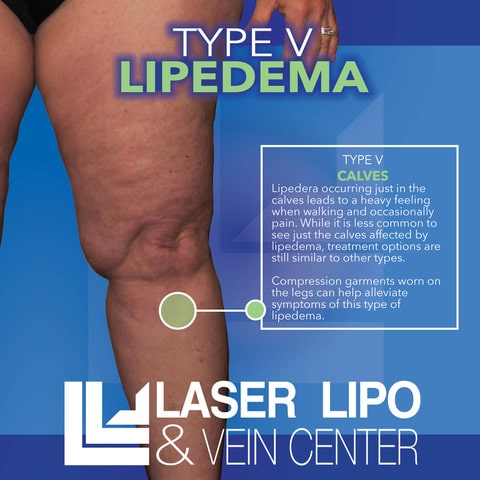
Type V: Calf Lipedema
Type V lipedema primarily affects the calves. This is the least common presentation of lipedema leading to an abnormal accumulation of fat in this in the calves and ankle. This type is the least common but still can significantly impact arm appearance and function.
Mixed Lipedema Presentations
Some individuals may exhibit a combination of different types of lipedema, with fat accumulation occurring in multiple areas of the body. Common mixed presentations are Type 3, 4 and Type 2, 4 Lipedema. This mixed presentation further emphasizes the heterogeneity of the condition.
Symptoms of Lipedema
Lipedema presents with a range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. The following are common indicators of lipedema:
- Enlarged hips, buttocks, and legs, with a disproportionate appearance compared to the upper body.
- Sensitivity to pressure and touch in the affected areas leading to pain and easy bruising.
- Swelling in the legs and affected areas, which worsens throughout the day or in hot weather.
- Spider veins or varicose veins may be present in the affected regions.
- The skin and tissues may feel soft, flexible, and colder in the affected areas.
- Small lumps, known as lipomas, may be felt within the enlarged tissues.
- Heavy, tired, and aching sensations in the legs and arms.
It is important to note that while these symptoms are frequently associated with lipedema, a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Managing Lipedema
While there is currently no cure for lipedema, various treatment approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans may involve a combination of conservative measures and surgical interventions, depending on the individual’s specific needs. The following strategies are commonly employed in the management of lipedema:
Conservative Lipedema Treatment Measures
- Compression therapy: Wearing custom-made compression garments can help reduce swelling and promote proper fluid circulation.
- Manual lymphatic drainage: This specialized massage technique can assist in reducing fluid swelling and improving lymphatic flow.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and movement therapies tailored to the individual’s needs can help improve mobility and reduce pain.
Surgical Interventions
- Lymphatic SparingTumescent Liposuction also known as Lipedema Reduction Surgery: This surgical procedure involves the removal of excess fat deposits and fibrotic tissue using a gentle suction technique. Lymph Sparing Tumescent liposuction is considered the most effective treatment for lipedema and can provide long-lasting results.
- Manual Lipedema Nodule Extraction: In some case, the fibotic nodules in the subcutaneous lipedema tissue may need to be removed with manual extraction. This is usually done at the same time as Lipedema Reduction Surgery or Lymph Sparing Liposuctionm if the nodules remain.
- Open Surgical Skin Reduction: In cases where there is significant skin and fat excess, reductive surgery may be recommended to remove the excess tissue and improve body contour.
- Combined surgical approaches: Some individuals with lipedema may benefit from a combination of tumescent liposuction and reductive surgery to achieve optimal outcomes.
Living with Lipedema
Living with lipedema can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. The impact of lipedema on body image, mobility, and overall well-being should not be underestimated. It is essential to seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones to navigate the complexities of this condition. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can contribute to overall well-being.
Seeking Proper Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect that you may have lipedema, it is crucial to seek a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional experienced in the management of this condition. They can evaluate your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs. Remember, early intervention and proper management are key to controlling symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Lipedema is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in specific areas of the body. Understanding the stages, types, and symptoms of lipedema is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. By seeking proper medical attention, individuals with lipedema can access the necessary support and treatment options to alleviate symptoms, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being. Remember, you are not alone in your journey, and there is hope for a fulfilling life with lipedema.
References:
Buck DW 2nd, Herbst KL. Lipedema: A Relatively Common Disease with Extremely Common Misconceptions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4(9):e1043. Published 2016 Sep 28. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000001043
Crescenzi R, Marton A, Donahue PMC, Mahany HB, Lants SK, Wang P, Beckman JA, Donahue MJ, Titze J. Tissue Sodium Content is Elevated in the Skin and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Women with Lipedema. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018 Feb;26(2):310-317. doi: 10.1002/oby.22090. Epub 2017 Dec 27. PMID: 29280322; PMCID: PMC5783748.
Forner-Cordero I, Olivan-Sasot P, Ruiz-Llorca C, Munoz-Langa J. Lymphoscintigraphic findings in patients with lipedema. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2018;37(6):341-8. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2018.06.008. Epub Aug 28.
Gould DJ, El-Sabawi B, Colletti PM, Patel KM. Abstract: Uncovering Lymphatic Transport Abnormalities in Patients with Lipedema. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5(9 Suppl):215. Published 2017 Oct 2. doi:10.1097/01.GOX.0000526475.17829.6b
Meier-Vollrath I, Schneider W, Schmeller W. Lipödem: Verbesserte Lebensqualität durch Therapiekombination. Dtsch Ärztebl 2005; 102: A 1061-1067.
Meier-Vollrath I, Schneider W, Schmeller W. Lipödem: Verbesserte
Lebensqualität durch Therapiekombination. Dtsch Ärztebl 2005; 102: A 1061-1067.