

Have you ever heard of lipedema? It’s a condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It causes an abnormal buildup of fat cells in the legs, buttocks, and hips, which can lead to pain, discomfort, and even disability. While there are several treatment options available, liposuction has become a popular choice among patients. However, not all liposuction procedures are the same. In fact, there are two distinct types of liposuction that are often confused: lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction.
Understanding the key differences between these two procedures is essential for anyone considering liposuction for lipedema or cosmetic purposes. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction and explain what sets them apart. So, whether you’re a patient or a healthcare provider, keep reading to discover the crucial distinctions between these two types of lipo.
Lipedema is a chronic condition that affects mainly women, although it can occur in men as well. It’s characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat and fibrous tissue in the legs, hips, and buttocks, which can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness. Lipedema is often misdiagnosed as obesity, lymphedema, or cellulite and can be a source of emotional and physical distress for those affected. As it progresses, Lipedmea can cause impairment in lymphatic function in the affected areas. There’s no cure for lipedema, but several treatment options are available, including liposuction.
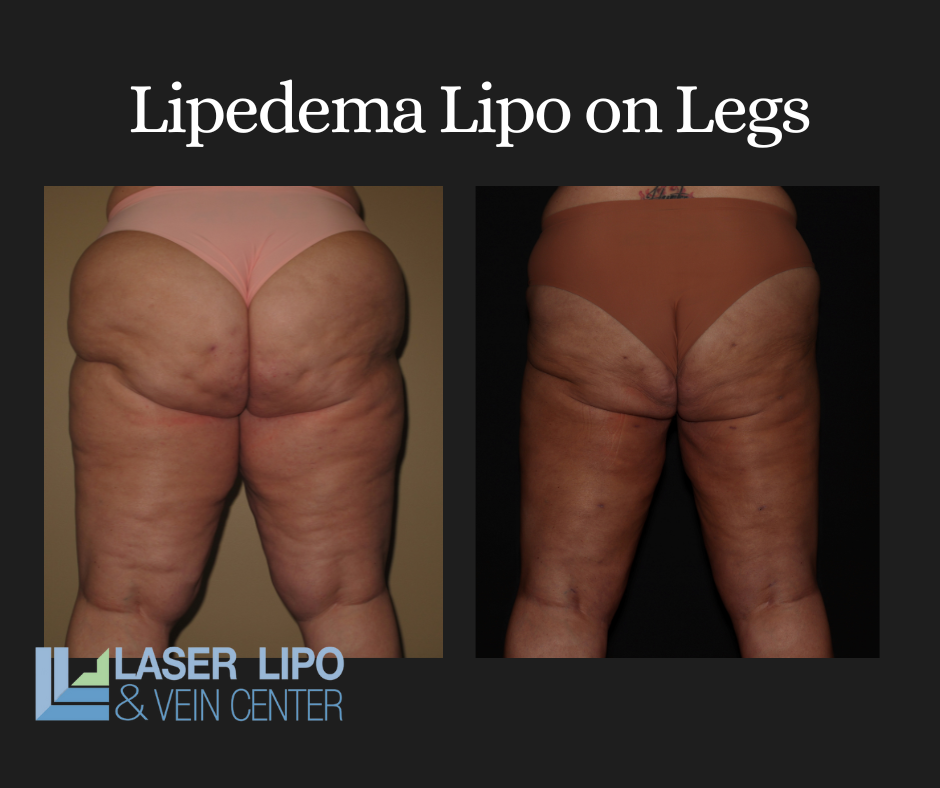

Lipedema liposuction is a specialized type designed to address the unique needs of lipedema patients. Unlike traditional cosmetic liposuction, which focuses on removing excess fat for aesthetic purposes, lipedema liposuction aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, and prevent further progression of the condition. Lipedema liposuction requires generous tumescent anesthesia and involves making small incisions in the affected areas. The surgeon then uses a specialized cannula to remove the excess fat cells while preserving the healthy tissue. The procedure can take several hours, depending on the extent of the lipedema.
One of the key differences between lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction is that lipedema liposuction is the extra surgical technique used to protect the lymphatics, sometimes called “lymph sparing.” It also may require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results. Lipedema is a chronic condition that can’t be cured with a single procedure. Lipedema patients may also require ongoing maintenance sessions to prevent further progression. Often Lipedema Lymph Sparing liposuction is combined with Manual Extraction of the fibrous nodules caused by the lipedema disease.
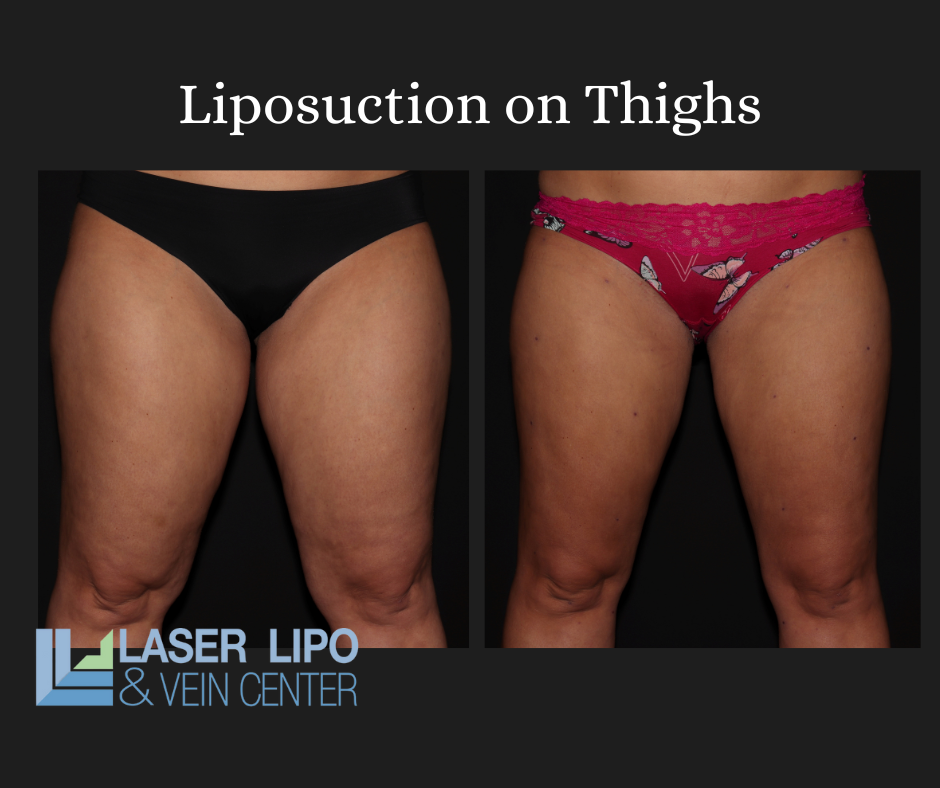

Cosmetic liposuction, also known as traditional liposuction, is a popular cosmetic procedure that’s designed to remove excess fat cells from various areas of the body, including the abdomen, thighs, and arms. Unlike lipedema liposuction, which is performed for medical reasons, cosmetic liposuction is performed for aesthetic purposes only.
While lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction are both forms of liposuction, there are several key differences between the two procedures. Some of the most significant differences include the following:
Like any surgical procedure, lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction carry some risks and side effects. Some of the most common risks and side effects include:
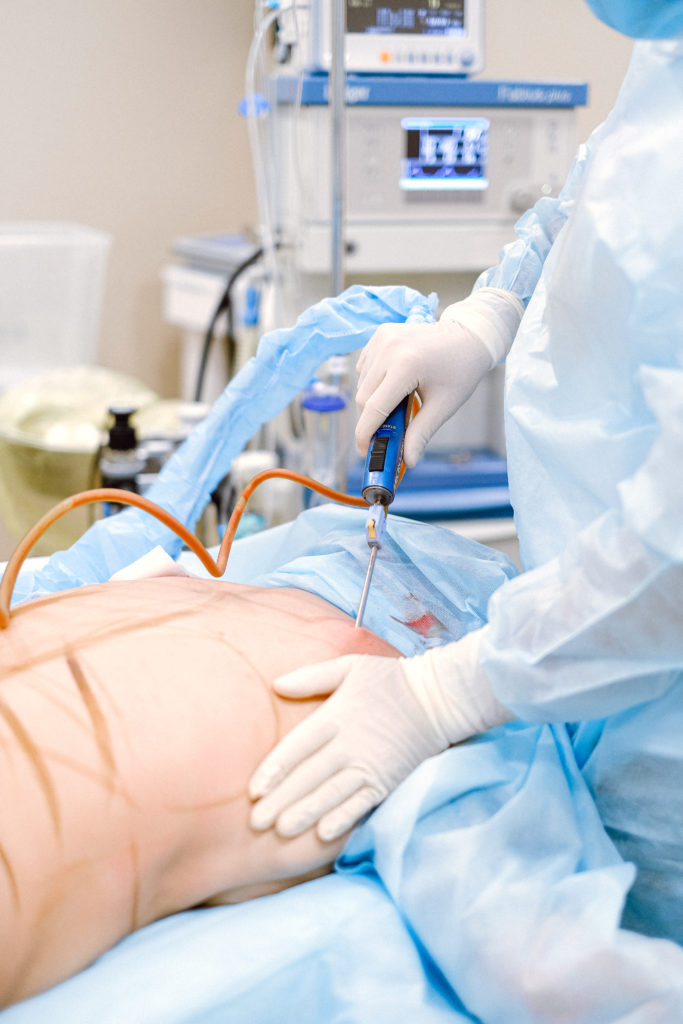

Recovery time and results can vary depending on the extent of the procedure and the patient’s individual health status. In general, patients can expect to experience some discomfort and swelling for several weeks after the procedure.
Patients undergoing lipedema liposuction may require compression garments and lymphatic massage to reduce swelling and promote healing. They may also need to avoid strenuous exercise and other activities for several weeks after the procedure.
Patients undergoing cosmetic liposuction can typically resume normal activities within a few days of the procedure. They may need to wear compression garments for several weeks to reduce swelling and promote healing.
Results from both procedures can be long-lasting, although patients need to maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent further weight gain and the progression of lipedema.
Lipedema liposuction is typically recommended for patients with advanced lipedema who have not responded to other treatments, such as compression therapy and diet modifications. Candidates for lipedema liposuction should be in good overall health and have realistic expectations of the procedure.
Cosmetic liposuction is typically recommended for patients who are at or near their ideal weight but have stubborn areas of fat that are resistant to diet and exercise. Candidates for cosmetic liposuction should be in good overall health and have realistic expectations of the procedure.
Choosing the right surgeon for lipedema liposuction or cosmetic liposuction is crucial for achieving the best possible results. Patients should look for a surgeon who has experience in performing the procedure, a proven track record of patient outcomes, and a good reputation in the community. Lipedema is a disease that requires specialized knowledge and comprehensive treatment, including dietary counseling and medical-grade compression to optimize lymphatic function. Pre and post-surgery treatment are focused on lowering tissue inflammation and controlling the disease comprehensively for the best results.
Many plastic surgeons approach lipedema reduction surgery as an isolated surgical procedure and need to treat lipedema comprehensively, which can result in suboptimal results or recurrence of symptoms. It is highly recommended to choose a surgeon who treats lipedema disease comprehensively. Patients should seek a surgeon who diagnoses the disease and starts conservative treatment first. A surgeon who treats comprehensively will ensure conservative treatment has been optimized, as proceeding with surgery when inflammation is elevated can actually worsen the disease course. Once the proper overall treatment plan has been implemented, the surgeon should take the time to explain the procedure and answer any questions the patient may have.
The cost of lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction can vary depending on several factors, including the extent of the procedure, the surgeon’s experience, and the geographic location.
Lipedema liposuction can be more expensive than cosmetic liposuction due to the specialized technique and multiple sessions required. Patients should check with their insurance provider to see if the procedure is covered under their policy.
Lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction are two distinct types of liposuction that are often confused. While both procedures involve the removal of excess fat cells, they have different purposes, approaches, and techniques. Understanding the key differences between lipedema liposuction and cosmetic liposuction is crucial for anyone considering liposuction for medical or cosmetic reasons. Patients should consult with a board-certified surgeon to determine which procedure is right for them and to achieve the best possible results.
Lipedema is a fat disorder, mainly affecting women, that causes an enlargement of both legs due to deposits of fat under the skin. It’s characterized as a “progressive disorder,” meaning it generally gets worse over time. Sufferers living with lipedema experience easy bruising and tenderness, pain in the affected areas, and significant disability in daily life. In severe and more progressive cases, the trunk and upper body may also be affected, including the arms and upper back. Little is known about the disorder, and it’s often misdiagnosed and incorrectly treated as general obesity.
For anyone affected, diet and exercise alone aren’t effective ways to get rid of Lipedema fat; Lipedema fat has proved relatively immune to these lifestyle changes and won’t budge. While women are likely to experience some weight loss with a healthy diet and regular exercise routines, weight loss is usually mostly loss of non-Lipedema fat. In these instances, the painful, stubborn fat remains. This cycle becomes a difficult one to break for those with the disorder: Yo-yo dieting leads to more weight gain. More weight gain leads to increased pain and disability. Increased pain and disability make it more challenging to manage mobility and secondary obesity increases. Lipedema fat also appears to be relatively resistant to bariatric surgery, meaning many women are undergoing dangerous surgeries without experiencing the intended benefit of significant loss of lipedema fat.
Unlike common obesity, Lipedema is comprised of fat deposits and swelling that typically does not affect the feet or hands; it’s as if patients are wearing a tight bracelet or rope at their wrists or ankles that causes every above to swell and everything below to remain unaffected. At more progressive stages, the swelling increases and leads to a diagnosis of lymphedema, which makes it even less likely Lipedema is diagnosed and treated promptly and adequately.
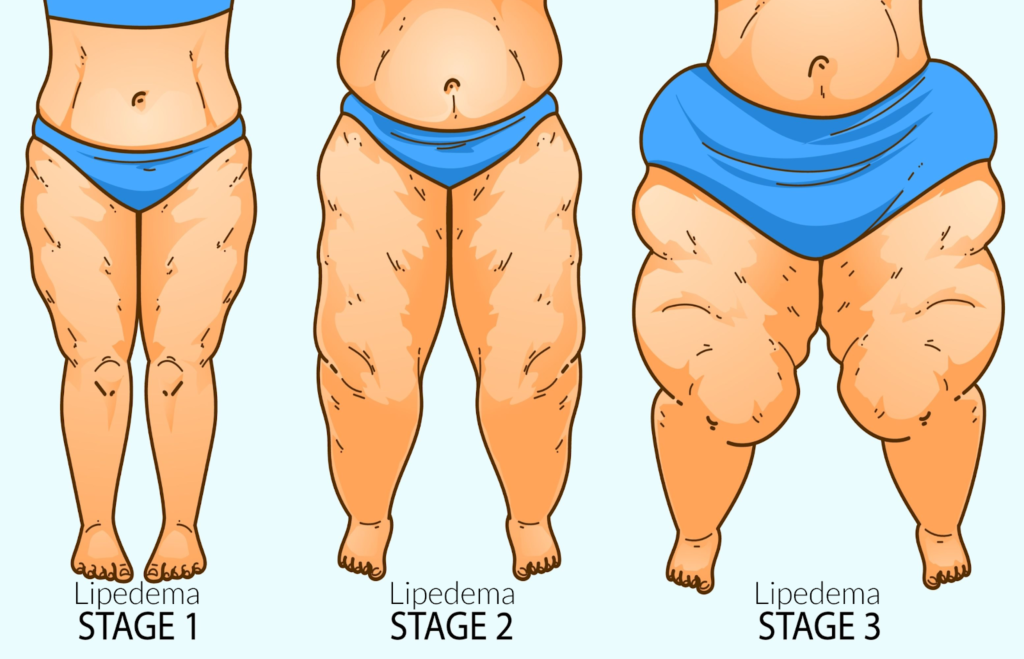

Despite the strong impact of Lipedema on millions of women across the world, only limited research exists to determine its cause. In many cases, the genetic background can provide some context, but enough research has yet to offer a comprehensive understanding of the disease.
Dr. Wright and his team at St. Louis Laser Lipo & Vein Center have put together a helpful list of Lipedema Do’s and Don’ts for living with this difficult disease.
Guaifenesin, best known by the brand name Mucinex©, and often prescribed as an over-the-counter expectorant to treat the common cold, may help reduce lipedema swelling and inflammation.


To our knowledge, there are no published, controlled studies showing the use of Guaifenisn to treat lipedema or lymphedema. However, there are abundant reports from clinicians and lipedema patients stating Guaifenisn helps lipedema. In our limited clinical experience, about 20 – 30 % of lipedema patients report reduced pain and/or swelling when taking this medication. Plus, there are reports of Guaifenisn being used for pain relief to treat other diseases. Guaifenesin has shown modest but significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects in neck and back pain and some other conditions. It is thought guaifenesin may be working as a muscle relaxant effect that occurs in these conditions. Mucinex / guaifenesin may help pain or it may work as an expectorant in lipedema tissue and thin out extracellular proteins. However, there are no studies to support these theories in lipedema.
Guaifenesin is approved for safe use at 600 mg twice a day (or 1,200 mg twice a day) for no more than 2,400 mg per day. Studies in the use of Mucinex for other medical conditions report it takes a least a week to see effects. I recommend lipedema suffers try this medication for two weeks to see if they notice any positive changes in addition to their consistent treatment plans including compression, supplements, and a healthy diet as prescribed. May not be suitable for people with a persistent cough due to asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, or smoking, or who have a cough that is producing excessive amounts of phlegm. Talk with your doctor first before using Mucinex if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Diosmin is a flavonoid extract made from orange peels used to treat vein disease. Diosmin helps reduce inflammation along vein walls in people with chronic venous insufficiency and it can also have very positive results for people with lipedema and lymphedema.


Benefits
In a recent case study, Diosmin had positive results when used in combination with other supplements, diet, compression, and other anti-inflammatory measures to non-surgically manage lipedema. Based on these studies, and my experience prescribing Diosmin to patients, I recommend Diosmin as part of an overall conservative management treatment plan for lipedema and lymphedema.
In the United States, Diosmin is sold under the brand name Vasculera, which is available in pharmacies by prescription from a physician. Vasculera is approved by the FDA as a medical food.
Diosmin is also available as a supplement without a prescription. We recommend Vein Formula, as we trust its formulation. Be sure to order any supplements from a reputable website for the best safety and quality. Link https://vitasupportmd.com/products/vein-formula-1000
Fat freezing—also known as cryolipolysis (or Cool Sculpting) uses cold temperature to reduce fat deposits in certain areas of the body. The procedure is designed to reduce localized fat deposits that do not respond to diet and exercise. It is not intended for people who are obese or significantly overweight. Currently, there is no published research on cryolipolysis for lipedema. Most lipedema fat is not the type of localized fat deposit for which this procedure is intended. Cryolipolysis can cause Paradoxical Adipose Hyperplasia (PAH). This condition can aggravate symptoms, and lead to worsening of lipedema.
Researchers from Stanford University found both diets improved blood glucose and led to comparable weight loss. However, this study shows keto may elevate LDL cholesterol, lacks essential nutrients, and is more difficult to maintain over time.


Study: During the study, 30 adults with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes followed the Mediterranean diet and the keto diet for 12 weeks each. Both diets served non-starchy vegetables and avoid added sugars and refined grains, but there are three key differences between them: the Mediterranean diet incorporates legumes, fruits, and whole grains – keto does not.
Note: Please work with a doctor or nutritionist to choose a dietary pattern that fits your needs and preferences. The potential harms of higher LDL associated with keto cannot be dismissed.
Exercising can help to activate the lymphatic drainage system in a patient’s limbs through the foot and calf muscle pump. Workouts that aren’t too strenuous help to move the excess fluids out of affected limbs, as well as reduce additional fat buildup.
The lymphatic system differs from the blood circulatory system in that it does not have a muscle “pump” to move fluids into the lymphatic system and eventually return back into circulation. Because of this, good lymph flow depends on proper joint and muscle activity. This is especially true if the lymphatic system is compromised. Individuals suffering from lipedema can receive a great benefit when engaging in diaphragmatic breathing exercises. These exercises are especially beneficial when they are combined together with other parts of a decongestive regimen.
Because fat disorders and lymphedema can often feed into one another, exercise is a great option to help combat both. With its dual purpose of clearing out excess lymph fluid and burning fat, exercise offers exactly what patients need to deal with these disorders.


The types of exercise used should be focused on the individual patient’s needs and ability. Additionally, it is important to use compression garments when exercising whenever possible. Compression garments help to promote blood circulation and lymph fluid flow, which can be severely inhibited in patients who suffer from fat disorders and lymphedema.
Even with all the challenges presented by lipedema, there are those who you can trust. Dr. Wright continues to strive for better education, research, and coverage for the lipedema community. Do not let these challenges bring you down even further; let Dr. Wright and his expert team help you to reduce the symptoms of lipedema and live your life fully! Dr. Wright can help find the right procedure to help manage your lipedema symptoms. Don’t let lipedema take over your life; contact us today!
Albert-Adrien Ramelet, MD, Pharmacologic Aspects of a Phlebotropic Drug in CVI-Associated Edema
First Published January 1, 2000
Scholar.google Diosmin Effect on Lymphatic Function
A lymphatic function of Daflon 500 mg
Int Angiol. A lymphatic function of Daflon 500mg., 1995 Sep; 14(3 Suppl 1):36-8
Recommended Sources for Diosmin: Vitasupport MD